How to Transport Patients to Hospital Beds Safely
How to safely transport patients to Hospital Beds?Transferring patients in nursing can be tricky. You need to ensure the patient is comfortable and safe while also avoiding injury to yourself. Whether it’s after surgery, illness, or weakness, using the right transfer methods is crucial. From my experience, using proper tools not only lowers the risk of injury for the patient but also protects your back and joints. In this guide, I’ll share the best techniques and equipment I’ve found, so you can make transfers safer and smoother.
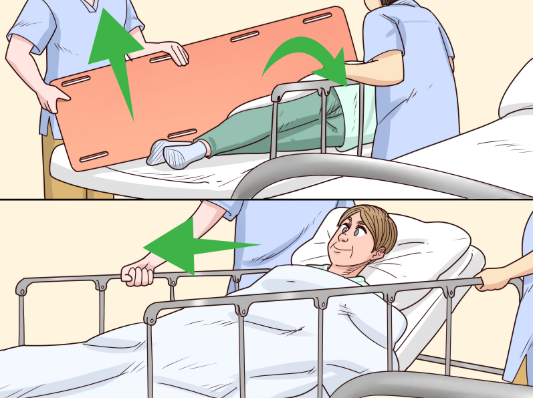
Patient Transfer Board
A patient transfer board is a useful tool that helps move patients from one surface to another, like from a hospital bed to a wheelchair or stretcher. It’s usually made of plastic or wood and creates a smooth, stable surface to reduce friction during the transfer.

How to Use a Patient Transfer Board
- Preparation: Make sure the patient is stable. Check that the area is clean and free of obstacles.
- Positioning the Board: Place one end of the board at the edge of the patient’s bed, and the other end on the target surface, like a wheelchair or another bed.
- Collaborative Transfer: If the patient can assist, encourage them to slide across the board. If not, caregivers should work together to gently guide the patient across to ensure a safe transfer.
Safety Tips for Using a Transfer Board
- Minimize Contact: Caregivers should avoid touching the patient’s body directly. Use the board to keep physical contact to a minimum.
- Proper Alignment: Make sure the board is flat and aligned with the bed or wheelchair to avoid tilting or shifting during the transfer.
Emergency Transfer Docking Trolley
The emergency transfer docking trolley helps move critically ill patients quickly and safely to Hospital beds. It is often used in intensive care units (ICUs) and recovery rooms to ensure smooth transfers with minimal risk. Its main purpose is to keep patients comfortable while reducing strain on caregivers.
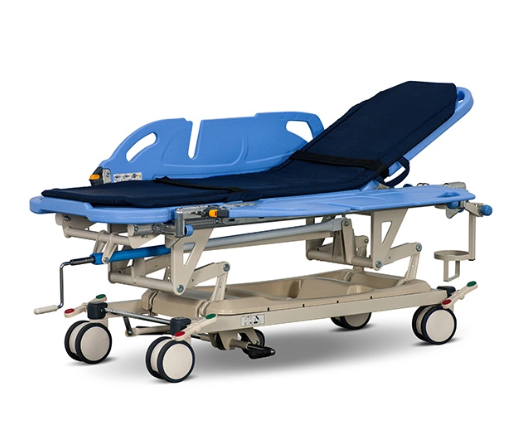

Key Features and Benefits
- Fast Patient Transfer – The trolley connects easily to hospital beds, making urgent transfers efficient.
- Stable and Secure – A locking mechanism keeps it in place during transfers, preventing sudden movements.
- Caregiver-Friendly Design – The ergonomic structure makes handling easier and reduces physical effort.
How to Use
- Get the Trolley Ready – Lock the wheels and engage the safety mechanism to prevent movement.
- Move the Patient Safely – Use straps or support belts if needed. Keep the head, spine, and limbs stable.
- Ensure a Smooth Transfer – Adjust the trolley and bed to the same height to avoid jolts. Multiple caregivers may be needed.
Safety Tips
- Match Heights – The trolley and bed must be level to prevent discomfort or injury.
- Watch Key Areas – Protect the patient’s chest, spine, and respiratory system from unnecessary pressure.
- Use Proper Support – Patients with mobility issues need extra transfer aids for stability.
Following these steps ensures that patient transfers are safe, smooth, and comfortable.
Hospital Bed with Adjustable Height
Modern hospital beds have an adjustable height feature that makes patient care and transport easier. Caregivers can raise or lower the bed to reduce strain and lower the risk of injury. This also helps both the patient and caregiver during transfers.
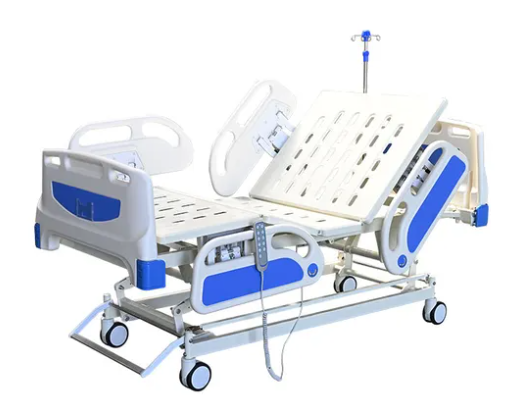
How to Use:
- Adjust the Bed Height: Set the bed to a comfortable level for both the patient and caregiver. This prevents strain and makes transfers safer.
- Secure the Patient’s Position: After adjusting the height, make sure the patient is in a stable and comfortable position. If needed, use support tools.
- Transfer Smoothly: Align the bed with the target surface to make the transfer easy and safe.
Safety Tips:
- Always lock the bed before adjusting the height to prevent movement.
- Talk to the patient throughout the process to help them feel at ease.
Nursing Considerations During Patient Transfer
|
Considerations |
Details |
|---|---|
| Patient Assessment |
Assess the patient’s physical condition, mobility, and pain tolerance before the transfer. If the patient experiences severe pain or discomfort, stop the transfer and consult a doctor to avoid further complications. |
| Teamwork for Safe Transfers |
If the patient is too weak or unable to help, two or more caregivers should assist to ensure safety. Do not attempt a single-person transfer for patients with limited mobility. This can cause harm to both the patient and the caregiver. |
| Use of Assistive Devices |
Use assistive devices like transfer belts or slings for patients with mobility issues to improve stability and safety. Make sure to handle and position the devices correctly to prevent strain or discomfort for the patient. |
| Maintaining Patient Privacy and Dignity |
Protect the patient’s privacy during the transfer by covering exposed areas. Keep open communication with the patient to ensure they feel comfortable and respected. |
Grace Medy as a hospital furniture manufacturer,supplies these tools for transferring patients. Grace Medy not only produces Height-adjustable hospital beds, but also provides supporting hospital furniture, rehabilitation equipment, such as operating tables, operating lights, medical carts, emergency trolleys, transfer boards, Wheelchairs, walking aids and more.
Conclusion
When moving patients to hospital beds, it’s important to have a clear plan, the right equipment, and the proper techniques. I’ve found that using transfer boards, emergency trolleys, and adjustable beds can make a big difference in preventing discomfort or injury. This makes the process smoother for both the patient and caregiver.
Key Considerations for Safe Patient Transfer:Use the Right Equipment: Transfer boards and trolleys provide stability, reducing strain on both the patient and me. It’s like having a solid support system beneath you, guiding each step.
Follow Safe Techniques: Lifting and positioning properly is key. A sudden strain can be painful, so using the right techniques is vital. I also focus on my posture to avoid unnecessary aches.
Ensure Clear Communication: I always talk to the patient, explaining each step and reassuring them. This keeps them calm and prepared, and it helps me feel more in control of the situation.
Thorough Preparation: Before transferring, I take a moment to assess the patient and plan the steps carefully. A little foresight helps avoid problems and ensures the process goes smoothly.
With the right equipment and techniques, transfers feel natural and easy, reducing stress and keeping everyone safe and comfortable.
